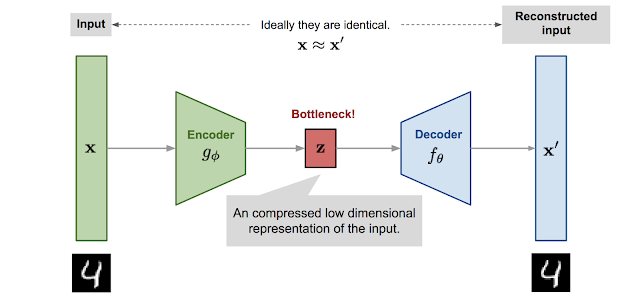
Understanding Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs)

Imagine being able to generate photorealistic 3D models of objects and scenes that can be viewed from any angle, with details so realistic that they are indistinguishable from reality. That's what the Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) is capable of doing and much more. With more than 50 papers related to NeRFs in the CVPR 2022, it is one of the most influential papers of all time. Neural fields A neural field is a neural network that parametrizes a signal. In our case, this signal is either a single 3D scene or an object. It is important to note that a single network needs to be trained to encode (capture) a single scene . It is worth mentioning that, unlike standard machine learning, the objective is to overfit the neural network to a particular scene. Essentially, neural fields embed the scene into the weights of the network. 3D scenes are usually stored in computer graphics using voxel grids or polygon meshes. However, voxels are costly to store and polygon meshes are lim...